In this topic Hide
RME provides comprehensive and flexible access controls for managing user access to pages, page actions, records, eForms and reports. For eForms, permissions also control when the user can see an eForm, and the actions that a user can perform. The high degree of flexibility for controlling access and permissions to different components means that there is a range of options for you to consider.
This high-level overview explains the different types of access, actions and permissions used in the RME environment and how they work together. Instructions and details about applying access and permissions are included in specific help pages or user guides where relevant.
![]() If you are new to RME, it may be a good
idea to read the other two help topics connected to this page. Click the
Next arrow in the top right corner
of this page to go to the next help page on this topic.
If you are new to RME, it may be a good
idea to read the other two help topics connected to this page. Click the
Next arrow in the top right corner
of this page to go to the next help page on this topic.
When setting up a new user or modifying access for an existing user, you need to think about the access they need to RME modules, specific pages, including eForm search pages, as well as eForm templates and reports. For both core records and eForms, you need to decide on the level of access they need and the actions they will need to perform.
The table below outlines the different types of access, actions and permissions you need to consider:
# |
Type of access | Description | Where you configure it |
1 |
Access to a set of predefined pages, actions, eForm templates and reports for a role |
Roles are set up for the different types of users for the system. A role is like a template for a particular position with predefined access to: 1a. Page Views for core and eForm pages in RME, and defined page actions 1b. eForm templates 1c. Reports When you assign a role to a user record, the access defined for that role will be automatically added for that user. This is more efficient than individually assigning access to each user. Roles are set up in RME > Users > Roles. A number of default roles are provided, shown in the Roles grid with a tick in the System? column. These are set up with a specific level of access to Page Views and some assigned page actions expected for the role. You can modify these to suit your needs by adding more Page Views, page actions as well as eForm templates and reports that you create. You can also create new roles from scratch. Default roles include: • Researcher • Student • Admin and data entry roles for all modules, such as Ethics Admin and Ethics Data Entry • RME Application Admin, with full access to the system See: Roles |
Assign a role: Configure a role: RME > Users > Roles ... Role Page Views ... eForm Template Access ... Report Role Access |
2 |
Access to specific pages |
• Page Views are commonly assigned via the role along with eForm templates and reports (as noted in 2. above). • When a user has a role assigned, you can also choose to assign specific Page Views in addition to those already defined for the role. • You can define what the user can do in each page you assign, from the following options: Full Access, Create-Edit Only, Edit-Only, or Read-Only. For details, see: Role Page Views |
RME > Users > Users > User Page Views |
2a.
Page Actions Tick the checkbox for each action you want to assign. Examples for core records: Allow Copy, Allow Versioning, Allow Bulk Update Examples for eForm pages: Allow Create Application, Allow Manage Application For details, see: Page View Actions |
RME > Users > Users > User Page Views |
||
3 |
Access to the RME system and to data (record, eForms) based on organisational units |
User log in credentials to be able to log in to RME and components
Options in the User record indicate the organisational level of access to data: • All Level User - access data for all org. units • Connection Account - access data for all org. units, designed for IT staff installing RME or using APIs, feeders or other integration services. This type of User account cannot log into RME via the front-end user interface. It is designed to connect in the backend for these types of services. |
RME > Users > Users
|
3a. Specific org. units defined in the User > Org. Units related item used to filter records by the user's Org. Unit and any child Org. Unit/s |
RME > Users > Users > Org. Units |
||
3b. External
users functionality enables those outside your institution to
register for an account and be assigned a defined role with limited
access to eForms, pages, and records. |
RME > System > System Preferences, External User Preferences |
||
4 |
Access to specific data based on code or type |
Restrict access to records and eForms based on specific codes or types: • 4a. Contract Type Code, for example, IP or Agreements • 4b. Ethics Category Code, for example, Animal, Human or Biosafety • 4c. Funding Activity Code, for example, Grants, Postgraduate (Scholarship), Commercialisation Project (core records only) • 4d. Project Type Code, for example, Grant, Consultation, Teaching and Learning |
RME > Users > Users > relevant related item |
5 |
Access to records that the user created |
The system automatically recognises any record or eForm that the user created and provides access to it (eForm access may be governed by workflow states). For HDR domains, eForms can be created on behalf of others. For details, refer to the RME eForm Designer User Guide. |
In-built system behaviour Not configurable |
6 |
Access to records that the user is linked to, for example, as a supervisor |
The system automatically recognises any record or eForm that the user linked to and provides access to it (eForm access may be governed by workflow states) |
In-built system behaviour Not configurable |
7 |
Restricted access to a page or section in an eForm (exception) |
Restrict access to a specific page or section of the eForm template by defining an exception to existing eForm permissions |
RME Designer > eForm Designer Refer to the RME eForms Administrators Guide |
8 |
Access an eForm when it is in a particular workflow state |
To define access permissions for the eForm for each state of the workflow for a user from a defined Participant or Custom Group: a) control the level of access, such as: Read only, Edit or Revision Edit b) workflow actions to control what users can do in an eForm in a particular state, such as review commenting, review outcomes and manage reviewers in a Review workflow state |
RME Designer > Workflow Designer Refer to the RME Workflow Designer User Guide |
9 |
Action to execute a workflow event |
To allow users to view and execute a workflow event, such as |
RME Designer > Workflow Designer Refer to the RME Workflow Designer User Guide |
The diagram below is a high-level, visual representation of how the different access and permissions outlined in the table above work together.
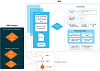
Click to view or hide: Overview of RME access, actions and permissions
Access_and_permissions_overview.htm